Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is one of the most critical indicators of a country's economic health.

For investors and swing traders, understanding and interpreting GDP data releases from the United States is crucial for making informed decisions regarding longer-term opportunities or developing risks.
What is GDP?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) represents the total monetary value of all goods and services produced over a specific time period within a country's borders. It is a comprehensive measure of a nation’s overall economic activity and is often used as an economic scorecard.
Components of US GDP

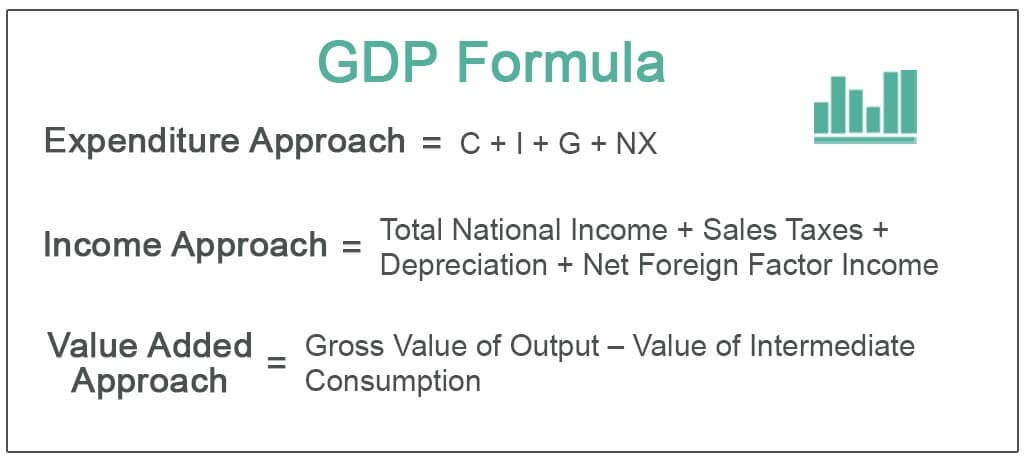
US GDP is mainly composed of four components:
Consumer Spending: The largest component, reflecting private expenditure.
Business Investment: Capital expenditures by businesses.
Government Spending: Public spending on goods and services.
Net Exports: Difference between exports and imports.
Understanding Nominal vs. Real GDP
When analyzing GDP data, it's crucial to differentiate between nominal GDP and real GDP. Nominal GDP, also known as current-dollar GDP, measures the value of all finished goods and services produced within a country's borders using current prices.
It does not account for inflation or deflation and can be misleading when comparing year-over-year economic performance. On the other hand, real GDP adjusts for inflation, providing a more accurate representation of economic growth.
Real GDP is calculated using constant prices from a base year, allowing for a comparison of economic output over time without the distortion of price changes. For investors and traders, focusing on real GDP is often more insightful, as it offers a clearer picture of an economy's actual growth and productive capacity.
This distinction is essential for making informed investment decisions, as it impacts the evaluation of economic health and potential investment opportunities.
Quarter-over-Quarter vs. Year-over-Year GDP Analysis
In the realm of GDP analysis, it's important to distinguish between quarter-over-quarter (QoQ) and year-over-year (YoY) comparisons. QoQ GDP growth measures the change in GDP from one quarter to the next, offering a granular view of economic performance and highlighting short-term trends or seasonal fluctuations.
In contrast, YoY GDP growth compares the GDP of a particular quarter to the same quarter in the previous year, smoothing out seasonal variations and providing a clearer picture of the long-term economic trend.
While QoQ data is valuable for understanding immediate economic shifts and the implications for quarterly earnings that we may see, year-over-year analysis is particularly crucial for long-term investment strategies, as it aligns better with the annual reporting periods of most corporations and gives a broader perspective on economic cycles and trends.
How to Read GDP Data Releases
1. First Look at the Headline Number
The headline GDP figure represents the annualized percentage change in the value of all goods and services produced. It is the real GDP growth number rate on a year-over-year basis.
Positive growth indicates an expanding economy, while negative growth suggests a contraction.
2. Understand the Type of Release
Advance Estimate: Released first, about a month after the quarter ends, but based on incomplete data.
Second Estimate: Includes more comprehensive data and is released a month later.
Final Estimate: Released another month later, provides the most complete data set.
3. Analyze the Components
Examine which components are driving or hindering economic growth.
Consumer spending trends can reflect confidence in the economy.
Business investment shows corporate sentiment and future capacity.
4. Look Beyond Seasonal Adjustments
US GDP data is seasonally adjusted to remove the effects of recurring seasonal patterns.
5. Compare with Expectations
Analysts provide GDP forecasts; compare the actual data with these expectations to gauge market reactions.
Importance for Interest Rate Setting
The Federal Reserve closely watches GDP data to make decisions on monetary policy, particularly interest rates. Strong GDP growth may prompt the Fed to raise interest rates to curb inflation, while weak growth could lead to rate cuts to stimulate the economy.
Implications for Investors
Interest Rate Sensitivity: Different asset classes react differently to interest rate changes.
Inflation Expectations: Strong growth often leads to inflation expectations, influencing bond yields and equity valuations.
Sector-Specific Impact: Some sectors are more sensitive to interest rate changes than others.
Earnings Impact: Economic strength or weakness often translates into corporate earnings and is worth watching.
GDP and Corporate Earnings
GDP data can be a precursor to corporate earnings:
Consumer Spending: High consumer spending can indicate robust earnings, particularly for consumer-facing companies.
Business Investment: Reflects corporate confidence and future growth prospects.
Economic Cycles: During expansion phases, companies typically report better earnings.
In Closing
Understanding GDP data is crucial for investors and swing traders as it provides a snapshot of economic health, influences monetary policy, and can signal corporate earnings trends. By dissecting the components and comparing them with market expectations, investors can better position their portfolios to capitalize on economic trends and mitigate risks.
Key Takeaways
GDP is a critical economic indicator reflecting the health of the economy.
Analysis of GDP data should involve a deep dive into its components and understanding the type of release.
GDP data significantly influences the Federal Reserve's interest rate decisions.
There is a strong correlation between GDP data and corporate earnings, impacting investment decisions.
For investors and swing traders, staying informed and understanding the intricacies of GDP data is an important. We may see trends taking shape, impacts that could translate to earnings growth or declines and other effects that can factor into our broader analysis of markets and the economy.
We’ll continue to monitor GDP and other data and key events to shape our views on the economy and implications for industries and sectors that may shape investment and trade opportunities for our Premium members.
